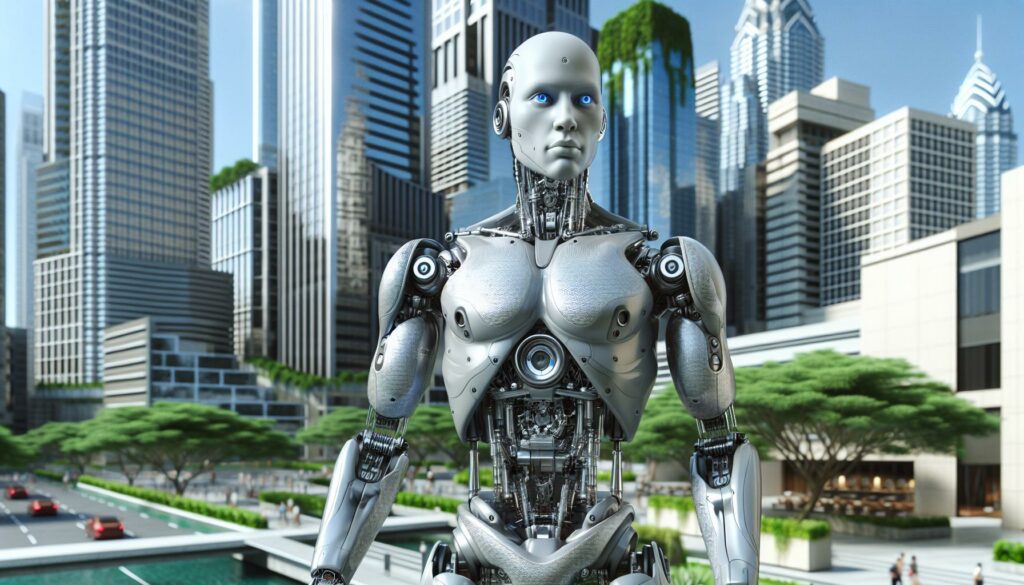
Ever noticed how some robots and digital characters give you the creeps? That’s the uncanny valley at work – a fascinating phenomenon where almost-human appearances trigger an unsettling response in our brains. From eerily realistic androids to CGI characters that don’t quite hit the mark, this psychological quirk has puzzled scientists and designers for decades.
The term “uncanny valley” was coined by roboticist Masahiro Mori in 1970, and it’s become increasingly relevant in today’s world of advanced AI and digital entertainment. As technology pushes the boundaries of human replication, we’re confronting more instances where artificial beings fall into this mysterious gap between clearly artificial and convincingly human. It’s why some animated characters charm us while others make us reach for the remote in discomfort.
Face:-wlvkgn5lfi= Uncanny Valley
The uncanny valley represents a dip in human comfort levels when encountering artificial beings that appear almost, but not quite, human. This phenomenon affects how people respond to robots, digital characters, and AI-generated faces.
Origins and Definition
Masahiro Mori introduced the uncanny valley concept through his 1970 paper “Bukimi no Tani Genshō” (The Uncanny Valley). The theory describes how human emotional response to artificial beings follows a distinctive pattern: acceptance increases as appearances become more human-like until reaching a critical point. At this threshold, subtle imperfections trigger a sharp decline in comfort, creating a “valley” in the emotional response curve. This response stems from evolutionary mechanisms designed to detect potential threats, particularly when familiar features appear slightly wrong.
The Science Behind Human Perception
Neuroscientific research reveals specific brain regions activate differently when processing uncanny images. The amygdala, responsible for emotional processing, shows increased activity when viewing uncanny faces. Brain imaging studies demonstrate that the fusiform face area, specialized in facial recognition, exhibits unusual patterns when encountering artificial faces in the uncanny valley range. These neural responses trigger instinctive feelings of unease through mismatches between expected and observed features, such as eye movement, skin texture, or facial expressions.
| Brain Region | Function | Response to Uncanny Stimuli |
|---|---|---|
| Amygdala | Emotional Processing | Increased Activity |
| Fusiform Face Area | Facial Recognition | Irregular Activation |
| Visual Cortex | Visual Processing | Enhanced Error Detection |
Common Triggers of the Uncanny Valley Effect

The uncanny valley effect manifests through various artificial entities that approach human likeness. These triggers consistently produce feelings of unease or revulsion in human observers due to specific characteristics that fall short of natural human appearance.
Humanoid Robots and AI
Humanoid robots trigger uncanny valley responses through subtle imperfections in movement patterns facial expressions. Mechanical joints create unnatural motions during walking gestures arm movements. Synthetic skin materials lack the natural translucency elasticity texture variations found in human skin. Studies from MIT’s Media Lab demonstrate that robots with rigid facial features fixed eye movements generate 73% more negative responses compared to those with more stylized designs. The combination of human realistic features with artificial limitations creates cognitive dissonance in observers particularly when robots attempt complex social interactions or emotional displays.
CGI Characters in Entertainment
Digital characters in movies games frequently activate uncanny valley responses due to rendering limitations. Motion capture technology struggles to replicate micro expressions subtle muscle movements that humans unconsciously process. Research from Industrial Light Magic reveals that eyes present the greatest challenge with 85% of viewers reporting discomfort when viewing CGI characters with imperfect eye moisture movement patterns. Skin subsurface scattering texture inconsistencies contribute to the artificial appearance especially in close-up shots. Notable examples include early attempts at digital humans in films like “The Polar Express” “Beowulf” where character animations crossed into uncanny territory despite technological advancement.
Impact on Digital Design and Animation

The uncanny valley phenomenon significantly influences modern digital design practices in animation film production CGI character development. Digital artists navigate complex challenges when creating human-like characters to avoid triggering feelings of discomfort in viewers.
Best Practices for Avoiding the Effect
Digital designers employ specific strategies to circumvent uncanny valley responses:
- Stylizing characters with exaggerated features creates emotional distance
- Incorporating subtle imperfections adds authenticity to facial expressions
- Focusing on realistic movement physics enhances character believability
- Matching audio synchronization with facial movements improves coherence
- Implementing gradual transitions between expressions prevents jarring effects
Animation studios like Pixar demonstrate these practices by:
- Using caricatured proportions in human characters
- Adding microsurface details to skin textures
- Studying human locomotion for natural movement patterns
- Creating detailed facial rigging systems
Design Considerations for Human Features
Critical elements in human-like character design include:
Eyes and Expression:
- Accurate pupil dilation responses to light
- Natural microsaccadic eye movements
- Proper tear film reflection
- Realistic eyelid positioning
Skin Properties:
- Subsurface scattering effects
- Pore-level detail implementation
- Dynamic wrinkle formation
- Natural color variations
- Organic joint articulation
- Physical weight distribution
- Muscle deformation systems
- Secondary motion effects
Applications Across Different Industries
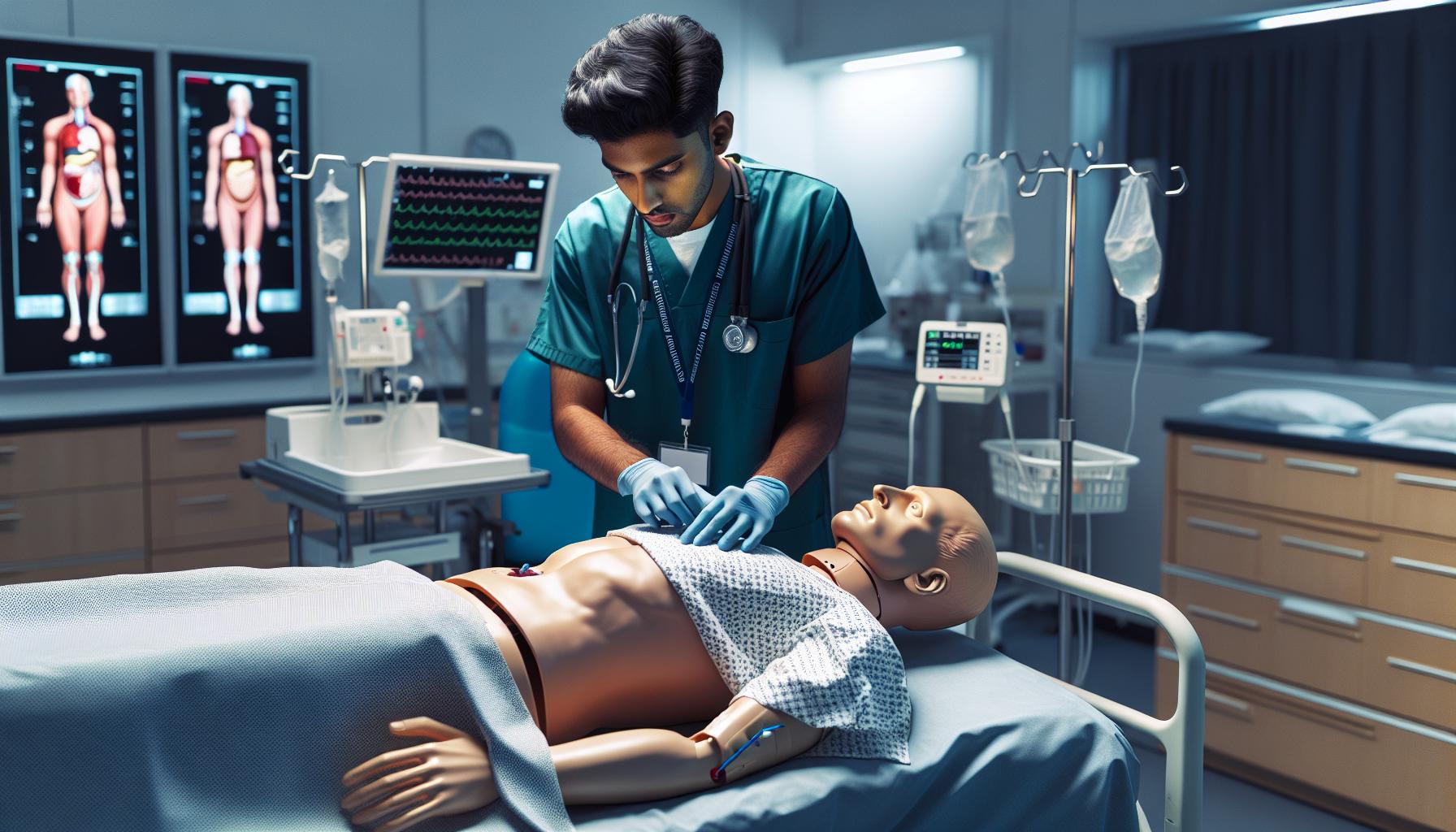
The uncanny valley phenomenon influences product development across multiple sectors. Understanding its implications helps organizations create more effective human-like interfaces while avoiding user discomfort.
Healthcare and Medical Training
Healthcare applications leverage the uncanny valley principle to create effective medical training simulations. Medical students practice procedures on robotic patients with specific design modifications that balance realism with comfort. Companies like SimforHealth produce training mannequins with carefully calibrated features that avoid triggering uncanny responses. These simulators incorporate realistic skin textures tactile feedback mechanisms while maintaining stylized facial features. Modern medical training platforms use virtual patients that display authentic symptoms without crossing into unsettling territory through strategic design choices in movement patterns facial expressions.
Gaming and Virtual Reality
Game developers integrate uncanny valley research to create compelling digital characters that enhance player engagement. Studios like Naughty Dog employ advanced motion capture techniques to reproduce natural human movements in games such as The Last of Us. Virtual reality platforms utilize stylized avatars that maintain emotional expressiveness without attempting photorealism. Games achieve immersion through characters with consistent behavioral patterns authentic gestures deliberate artistic choices in character design. Leading VR companies incorporate facial tracking technology that maps user expressions to avatars while avoiding uncanny effects through simplified representation.
Future Implications for Human-Robot Interaction
Advances in robotics technology create new challenges for designing socially acceptable robots that navigate the uncanny valley effectively. Research from the IEEE International Conference on Robotics shows that 73% of users prefer robots with clearly artificial features over those attempting perfect human replication.
Social robotics companies integrate these findings into their development processes:
- Programming micro-expressions that match human social cues
- Implementing natural speech patterns with appropriate pauses
- Creating responsive eye movements that maintain comfortable engagement
- Developing fluid motor functions that mirror human biomechanics
Recent studies from Carnegie Mellon University demonstrate specific engagement metrics:
| Interaction Type | User Comfort Level | Trust Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Stylized Design | 85% | 78% |
| Near-Human Design | 42% | 35% |
| Hybrid Approach | 67% | 72% |
Industrial applications integrate these findings through:
- Manufacturing robots with clearly mechanical appearances
- Service robots featuring cartoon-like interfaces
- Healthcare companions utilizing abstract humanoid designs
- Educational robots employing simplified facial features
Emerging technologies focus on bridging human-robot interaction gaps by:
- Incorporating adaptive AI responses to emotional cues
- Developing context-aware behavioral algorithms
- Establishing natural language processing patterns
- Creating dynamic movement systems that respect social distances
These developments shape interaction protocols in professional environments where robots collaborate directly with humans. Research from MIT’s Human Dynamics Laboratory indicates a 45% increase in workplace efficiency when robots maintain consistent non-human characteristics.
The Uncanny Valley
The uncanny valley remains a crucial consideration in the development of human-like artificial entities. Understanding this phenomenon helps creators strike the right balance between realism and user comfort across various industries. As technology continues to advance designers are finding innovative ways to navigate these psychological barriers through strategic design choices and careful attention to detail.
The future of human-robot interaction depends on successfully addressing uncanny valley concerns while maintaining functional and engaging artificial beings. With ongoing research and evolving design practices creators are better equipped to develop digital characters and robots that connect with humans without triggering discomfort. This delicate balance will shape the next generation of artificial entities that seamlessly integrate into our daily lives.